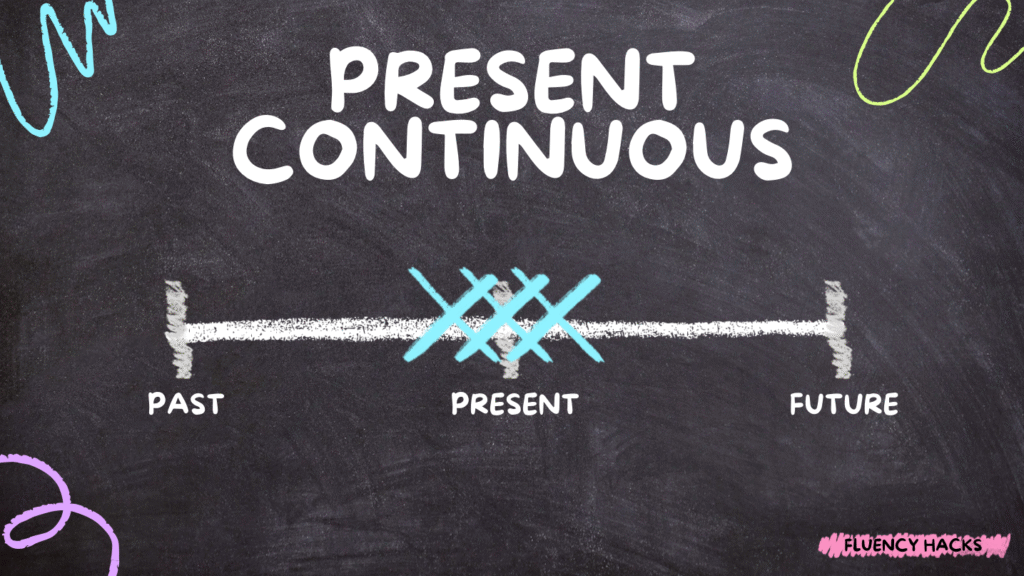
O Present Continuous (ou Present Progressive) é um dos tempos verbais mais importantes e usados no inglês. Ele te ajuda a falar sobre ações que estão acontecendo agora.
Como é formado?
A estrutura é simples:
Sujeito + verbo to be (am/is/are) + verbo principal com -ing
| Sujeito | Verbo ‘to be‘ | Verbo principal com -ing |
| I | am | working |
| You | are | studying |
| He | is | playing |
| She | is | talking |
| It | is | sleeping |
| We | are | cooking |
| They | are | eating |
Exemplos:
✅ I am studying now.
✅ She is cooking dinner.
✅ They are watching a movie.
Quando usar o Present Continuous?
✔️ Ações que estão acontecendo agora
Ex.: I’m talking to you right now.
Present Continuous — Negative Form
Sujeito + verbo to be (am/is/are) + not + verbo principal com -ing
Exemplos:
✅ I am not working. | I’m not working.
✅ You are not studying. | You’re not studying. | You aren’t studying.
✅ He is not playing. | He’s not playing. | He isn’t playing.
✅ She is not talking. | She’s not talking. | She isn’t talking.
✅ It is not sleeping. | It’s not sleeping. | It isn’t sleeping.
✅ We are not cooking. | We’re not cooking. | We aren’t cooking.
✅ They are not eating. | They’re not eating. | They aren’t eating.
Present Continuous — Interrogative Form
Verbo to be (am/is/are) + sujeito + verbo principal com -ing
Exemplos:
✅ Am I dreaming?
✅ Are you studying?
✅ Is he playing?
✅ Is she talking?
✅ Is it sleeping?
✅ Are we cooking?
✅ Are they eating?
Verbos Estáticos — Stative Verbs
Normalmente, não usamos o tempo contínuo com verbos estáticos. Verbos estáticos incluem:
- Verbos de pensamento e sentimento — like, love, hate, prefer, believe, know, remember, want, understand, wish
- Outros exemplos — seem, matter, taste, sound, own
Dicas importantes
➡️ Não esqueça do verbo to be!
Muitos alunos pulam essa parte e acabam dizendo frases como:
❌ “She cooking now.”
✔️ “She is cooking now.”
➡️ Atenção aos ‘stative verbs’
Nem tudo adicionamos -ing, como:
❌ “I’m knowing the answer.”
✔️ “I know the answer.”
➡️ Use a forma -ing correta
Verbos terminados em -e (como make) perdem o -e antes de -ing:
make → making
write → writing
Verbos que terminam com “ie” (ex: “die”) trocam o “ie” por “y” e adicionam -ing.
die → dying
➡️ CVC — Consoante + Vogal + Consoante
No Present Continuous, quando um verbo termina em consoante + vogal + consoante (padrão CVC), e o acento tônico está na última sílaba, duplicamos a consoante final antes de adicionar -ing.
run → running
swim → swimming
begin → beginning
O Present Continuous é essencial para falar de ações do momento — e também em outras situações que abordaremos futuramente. Quer praticar? Escreva 3 frases sobre o que você está fazendo neste momento em inglês e compartilhe aqui!
💬 Gostou das dicas? Compartilhe com quem também está aprendendo inglês! ✏️




Deixe um comentário